Bulbs
Flower Basics
Flower Beds & Specialty Gardens
Flower Garden
Garden Furniture
Garden Gnomes
Garden Seeds
Garden Sheds
Garden Statues
Garden Tools & Supplies
Gardening Basics
Green & Organic
Groundcovers & Vines
Growing Annuals
Growing Basil
Growing Beans
Growing Berries
Growing Blueberries
Growing Cactus
Growing Corn
Growing Cotton
Growing Edibles
Growing Flowers
Growing Garlic
Growing Grapes
Growing Grass
Growing Herbs
Growing Jasmine
Growing Mint
Growing Mushrooms
Orchids
Growing Peanuts
Growing Perennials
Growing Plants
Growing Rosemary
Growing Roses
Growing Strawberries
Growing Sunflowers
Growing Thyme
Growing Tomatoes
Growing Tulips
Growing Vegetables
Herb Basics
Herb Garden
Indoor Growing
Landscaping Basics
Landscaping Patios
Landscaping Plants
Landscaping Shrubs
Landscaping Trees
Landscaping Walks & Pathways
Lawn Basics
Lawn Maintenance
Lawn Mowers
Lawn Ornaments
Lawn Planting
Lawn Tools
Outdoor Growing
Overall Landscape Planning
Pests, Weeds & Problems
Plant Basics
Rock Garden
Rose Garden
Shrubs
Soil
Specialty Gardens
Trees
Vegetable Garden
Yard Maintenance
How Do Leaves Help Photosynthesis?
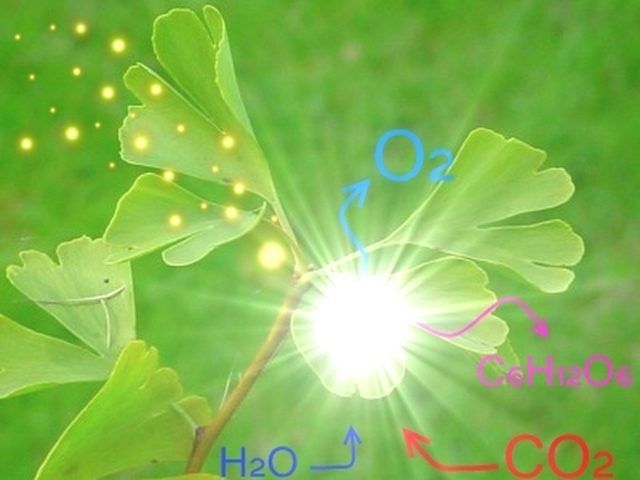
How Do Leaves Help Photosynthesis?. Photosynthesis provides a plant with a means of producing its own food from water, carbon dioxide, light and minerals. This process occurs in the chloroplasts, located in the green portions of the plant, including the leaves. The structure of the leaf aides in photosynthesis by helping the plant to acquire all of...

Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis provides a plant with a means of producing its own food from water, carbon dioxide, light and minerals. This process occurs in the chloroplasts, located in the green portions of the plant, including the leaves. The structure of the leaf aides in photosynthesis by helping the plant to acquire all of the required materials to manufacture its own food.
External Leaf Shape
Leaves best suited for photosynthesis have wide, flat green areas to allow for maximum exposure to light. Thin leaves allow for efficient transfer of carbon dioxide to the chloroplasts inside the leaves, which the plant uses with light to create food. Oxygen released as waste from photosynthesis rises to the surface best in a thin leaf and dissipates better from leaves with a large surface area of the leaves. The veins of the leaves carry water and mineral nutrients absorbed through the plant's roots throughout the leaves. This action provides the other requirements for photosynthesis not acquired by the leaves.
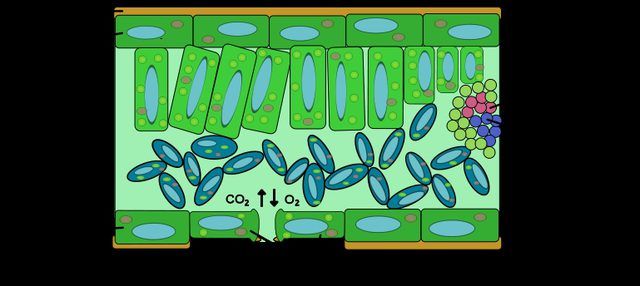
Internal Leaf Structure
In green plants, photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts. These reside inside the mesophyll cells sandwiched by a top and bottom protective layer of epidermis. The location of the mesophyll in the middle of the leaves allow them to get the sit in the path of carbon dioxide taken in by the leaf and give them an exit path for the wasted oxygen.