Bulbs
Flower Basics
Flower Beds & Specialty Gardens
Flower Garden
Garden Furniture
Garden Gnomes
Garden Seeds
Garden Sheds
Garden Statues
Garden Tools & Supplies
Gardening Basics
Green & Organic
Groundcovers & Vines
Growing Annuals
Growing Basil
Growing Beans
Growing Berries
Growing Blueberries
Growing Cactus
Growing Corn
Growing Cotton
Growing Edibles
Growing Flowers
Growing Garlic
Growing Grapes
Growing Grass
Growing Herbs
Growing Jasmine
Growing Mint
Growing Mushrooms
Orchids
Growing Peanuts
Growing Perennials
Growing Plants
Growing Rosemary
Growing Roses
Growing Strawberries
Growing Sunflowers
Growing Thyme
Growing Tomatoes
Growing Tulips
Growing Vegetables
Herb Basics
Herb Garden
Indoor Growing
Landscaping Basics
Landscaping Patios
Landscaping Plants
Landscaping Shrubs
Landscaping Trees
Landscaping Walks & Pathways
Lawn Basics
Lawn Maintenance
Lawn Mowers
Lawn Ornaments
Lawn Planting
Lawn Tools
Outdoor Growing
Overall Landscape Planning
Pests, Weeds & Problems
Plant Basics
Rock Garden
Rose Garden
Shrubs
Soil
Specialty Gardens
Trees
Vegetable Garden
Yard Maintenance
How Do Plants Store Excess Sugar?
How Do Plants Store Excess Sugar?. All living organisms are formed from units called cells. All cells contain DNA to create other cells. The cells are semipermeable, which means they allow some substances to get through the membrane and deny others access. Plant cells are a bit more complex. They have internal sub-sections known as organelles and...
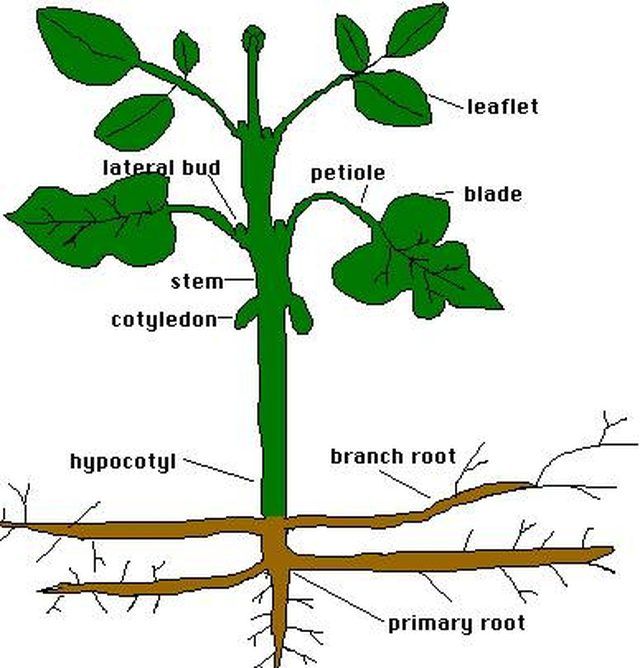
Plants, Cells, and Starch
All living organisms are formed from units called cells. All cells contain DNA to create other cells. The cells are semipermeable, which means they allow some substances to get through the membrane and deny others access. Plant cells are a bit more complex. They have internal sub-sections known as organelles and micro-fibers that form a cytoskeleton in a nucleus bound to the membrane which contains DNA. Unused sugars in plants are stored as starch. Starch is considered to be a complex sugar.
The Cell Wall
The cell wall of a plant has a barrier that the membrane presses against and that it uses to maintain a rigid structure. Inside of the plant, excess sugar is stored as starch. Starches are recognized as a major component of foods ingested into the human body, to be used as energy or stored as fat. Likewise, the plant uses these starches as stored food sources. In woody plant stems, starch is also stored for later use as energy. Trees are known to create sugar through photosynthesis; the unused sugar is transported through the phloem, stored in the trunk or roots as starch and then turned back into sugar to be used as energy again at the start of a new spring.
Glucose
The glucose units in plants are linked in linear bonds. Whenever plants need energy for cell work, they hydrolyze the stored starch, releasing the glucose subunits. The strategically branched polymer of glucose used in this process is known as amylopectin; it and amylose make up the two main components of starch. Starch itself is made of at least 70% amylopectin, constituting the bulk of the plant being used for energy storage.