Bulbs
Flower Basics
Flower Beds & Specialty Gardens
Flower Garden
Garden Furniture
Garden Gnomes
Garden Seeds
Garden Sheds
Garden Statues
Garden Tools & Supplies
Gardening Basics
Green & Organic
Groundcovers & Vines
Growing Annuals
Growing Basil
Growing Beans
Growing Berries
Growing Blueberries
Growing Cactus
Growing Corn
Growing Cotton
Growing Edibles
Growing Flowers
Growing Garlic
Growing Grapes
Growing Grass
Growing Herbs
Growing Jasmine
Growing Mint
Growing Mushrooms
Orchids
Growing Peanuts
Growing Perennials
Growing Plants
Growing Rosemary
Growing Roses
Growing Strawberries
Growing Sunflowers
Growing Thyme
Growing Tomatoes
Growing Tulips
Growing Vegetables
Herb Basics
Herb Garden
Indoor Growing
Landscaping Basics
Landscaping Patios
Landscaping Plants
Landscaping Shrubs
Landscaping Trees
Landscaping Walks & Pathways
Lawn Basics
Lawn Maintenance
Lawn Mowers
Lawn Ornaments
Lawn Planting
Lawn Tools
Outdoor Growing
Overall Landscape Planning
Pests, Weeds & Problems
Plant Basics
Rock Garden
Rose Garden
Shrubs
Soil
Specialty Gardens
Trees
Vegetable Garden
Yard Maintenance
How Does Osmosis Work?
How Does Osmosis Work?. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a plasma membrane (lipid bilayer). It is a form of active transport. The water molecules diffuse through a semi-permeable membrane, moving from areas of lower concentration of water molecules to areas of higher concentration of water molecules. It is the main way water is transported...


What is Osmosis?
Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a plasma membrane (lipid bilayer). It is a form of active transport. The water molecules diffuse through a semi-permeable membrane, moving from areas of lower concentration of water molecules to areas of higher concentration of water molecules. It is the main way water is transported in and out of cells.
Hypotonic Vs. Hypertonic
The areas of high concentration of water molecules are called hypotonic. Hypotonic solution has a low concentration of dissolved substances. Areas of low concentration of water molecules are called hypertonic. Hypertonic solution has a high concentration of dissolved substances. During osmosis, water molecules naturally travel from hypotonic areas to hypertonic areas. This process equalizes the concentrations of water and dissolved substances.
Active Transport
When ions and molecules move from lower to higher concentration areas, it is called active transport. Active transport requires energy and help from proteins to move substances against the concentration gradient in and out of a cell. Active transport is basically the opposite of simple diffusion.
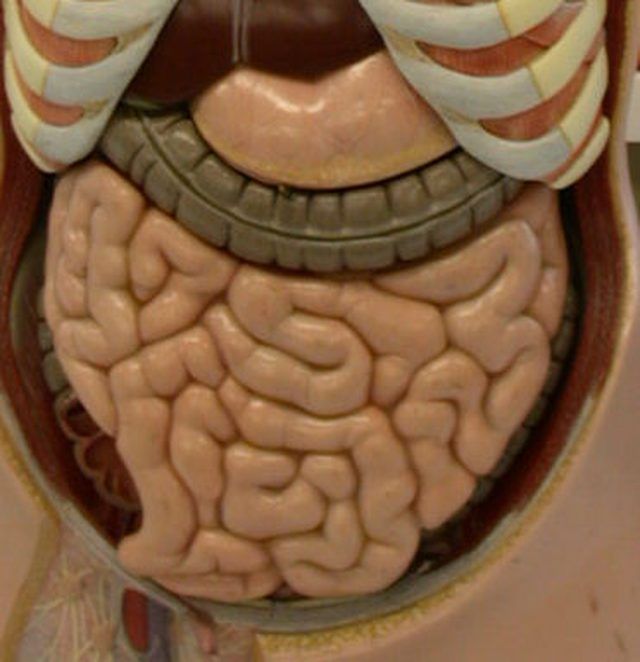
Osmosis in the Small Intestine
The small intestine is one place where osmosis is constantly occurring. The liquids you drink, as well as saliva and other liquids, are always being absorbed and secreted in the small intestine via osmosis. Sodium is what sets the gradient that water counters in the small intestine.
Facilitated Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion speeds up osmosis but isn't required for it. Facilitated diffusion occurs when transfer proteins make watery holes that molecules and ions can pass through. The cell can open or close those holes depending upon its needs. In osmosis, a semi-permeable membrane will not allow unlimited molecules and ions to pass through, only unlimited water molecules. Facilitated diffusion allows more molecules and ions to pass through the semi-permeable membrane than osmosis alone.